|
Sep 30, 2011, 07:39 PM
|
|
|
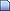
 Abnormalities in how the nucleus accumbens, highlighted here, processes dopamine have been found in individuals with psychopathic traits and may be linked to violent, criminal behavior.
Abnormalities in how the nucleus accumbens, highlighted here, processes dopamine have been found in individuals with psychopathic traits and may be linked to violent, criminal behavior.
Quote:
The brains of psychopaths appear to be wired to keep seeking a reward at any cost, new research from Vanderbilt University finds. The research uncovers the role of the brain's reward system in psychopathy and opens a new area of study for understanding what drives these individuals.
The results were published March 14, 2010, in Nature Neuroscience.
"Psychopaths are often thought of as cold-blooded criminals who take what they want without thinking about consequences," Joshua Buckholtz, a graduate student in the Department of Psychology and lead author of the new study, said. "We found that a hyper-reactive dopamine reward system may be the foundation for some of the most problematic behaviors associated with psychopathy, such as violent crime, recidivism and substance abuse."
Previous research on psychopathy has focused on what these individuals lack—fear, empathy and interpersonal skills. The new research, however, examines what they have in abundance—impulsivity, heightened attraction to rewards and risk taking. Importantly, it is these latter traits that are most closely linked with the violent and criminal aspects of psychopathy.
"There has been a long tradition of research on psychopathy that has focused on the lack of sensitivity to punishment and a lack of fear, but those traits are not particularly good predictors of violence or criminal behavior," David Zald, associate professor of psychology and of psychiatry and co-author of the study, said. "Our data is suggesting that something might be happening on the other side of things. These individuals appear to have such a strong draw to reward—to the carrot—that it overwhelms the sense of risk or concern about the stick."
|
http://www.sciencenewsline.com/biolo...401000017.html
Another interesting study offering a theory on the cause of psychopothy. As a comparison: http://www.psychiatrictimes.com/binary_content_servlet
|